| February 10, 2026
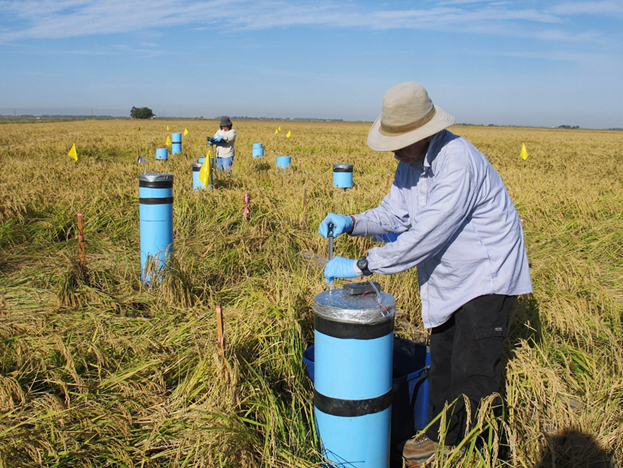
DASIG, which means “accelerate” in the Filipino language, started as a number of Python scripts design to automate the data processing and greenhouse gas flux calculations from long-term emission experiments using the Chamber Method, conducted on flooded rice in northeast Arkansas, USA.
The DASIG calculation procedures followed the field measurement and laboratory analysis protocols used by scientists at the USDA Delta Water Management Research Unit and collaborators at Arkansas State University, which evolved from decades of experience and scientific development conducted in the USA and other countries.
GHG flux calculations require substantial time and effort. They are usually done manually with the help of computer spreadsheets or scripts written for specific situations. This introduces inconsistencies in the calculation method and error estimates, leading to varied levels of quality control.
The DASIG model was developed to automate GHG flux and Global Warming Potential calculations through a desktop application that facilitates the management of field gas samples and trace gas analysis, and automates the determination of trace gas concentrations from gas chromatograph analyzers and the calculation of emission fluxes.
Each DASIG module consumes and produces Excel spreadsheets to report and document the flux calculation procedure. DASIG continues to be developed to include new features such as an Experiment Design module, better analysis and data visualization tools, and support for development of standardized GHG databases.
DASIG is currently being developed at the Arkansas State University.